You need to be very careful when choosing the motherboard for your PC, in this article we find out all the details of the case
The motherboard is the supporting pillar of every computer, a microscopic universe that houses a myriad of components essential for the functioning of the machine. It represents the meeting point between the outside world and the electronic heart of the PC, acting as a bridge between the various input/output devices and the processor, RAM memory and other crucial components. On BestialGames.it you can find a list of the best motherboards on the market with related reviews.
When we talk about motherboard components, we are referring to the collection of circuits and connectors that allow a computer to function and interact with the user. But what are the main components of a motherboard and how do they affect the performance of your PC? Let’s find out together on this journey inside the motherboard.
The heart of the motherboard: the Chipset
The chipset, often described as the beating heart of the motherboard, plays a crucial role in coordinating data traffic between various crucial components of the computer system, ensuring that all operations are performed smoothly and efficiently. It acts almost like an orchestra conductor, orchestrating communication between the processor, RAM, expansion cards, and storage devices.
The structure of the chipset is bipartite, mainly composed of two distinct but interconnected elements: the North Bridge and the South Bridge, each with well-defined responsibilities. The North Bridge is responsible for managing the data flow between the processor, RAM and video card. This component is essential as it facilitates high-speed interactions between these vital parts, ensuring that processing requests are handled promptly and data is transferred where needed without a hitch.
On the other hand, the South Bridge handles communications with input/output peripherals and data storage. This includes interfacing with devices such as hard drives, SSDs, USB ports, and other peripherals that require a constant but less intense data flow than that handled by the North Bridge. Harmony between the North Bridge and the South Bridge is imperative; precise synchronization between these two “bridges” is essential to ensure optimal functioning of the system. The effective coordination between these two elements allows you to avoid bottlenecks in data traffic, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and without interruptions, significantly contributing to the overall performance of the computer.
The different formats of motherboards
Motherboards are manufactured in a variety of formats, each designed to meet particular needs in terms of size, configuration and system expansion potential. These formats are essential to determine not only the aesthetic appearance of the PC, but also its performance and flexibility in terms of future updates.
1. ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is one of the most common formats and is known for its relatively large size that offers space for a greater amount of components and expansion slots, making it a solid choice for users who need systems high performance with many peripherals.
2. One smaller step down we find Micro ATX, which retains a good amount of the flexibility of ATX while being more compact, making it suitable for builds that require less expansion but want to maintain some robustness.
3. The Mini ATX is further reduced in size, and while it offers fewer expansion options, it is a cost-effective choice for environments with limited space.
4. Finally, Mini ITX is the smallest of the common formats, and is ideal for compact and portable systems, with an emphasis on energy-saving and efficient cooling solutions. Despite its small size, the Mini ITX doesn’t completely compromise performance, and can still accommodate a decent hardware configuration, albeit with obvious limitations compared to larger formats.
Each motherboard format has its place in the computing ecosystem, offering a unique balance of size, expansion capabilities, and performanceallowing users to build systems that perfectly fit their specific needs.
ATX e Micro ATX
ATX motherboards represent a consolidated norm in the computing landscape, ensuring an optimal balance between size, expandability and functionality. These motherboards have a larger surface area than other formats, making them ideal for accommodating more components and connectors. Thanks to these characteristics, ATX cards lend themselves to various applications, allowing users to assemble computer systems capable of satisfying a wide range of needs, from high-performance gaming to professional activities that require considerable computing power.
On the other hand, the Micro ATX variants, despite having small dimensions, maintain high quality and a good quantity of connectors and expansion slots. The reduction in size does not come at the expense of functionality, making Micro ATXs an excellent choice for those who have limited space or prefer a more compact system. Being slightly smaller, Micro ATXs are often considered more manageable and are particularly appreciated in those contexts where space is a critical factor. Both of these formats, ATX and Micro ATX, offer a solid platform for those looking for a good compromise between size, performance and expansion possibilities.
Their flexibility allows users to add or modify components in the future, such as expansion cards or other devices, without facing significant limitations. This way, users can enjoy some freedom in configuring theirs computer systemwhile ensuring that the case can accommodate all the components necessary to guarantee the desired performance.
Mini ATX is Mini ITX
Mini ATX and Mini ITX motherboards are perfect options for those looking for more compact solutions without sacrificing essential functionality. Despite their small size, these motherboards are capable of supporting the construction of a PC powerful and versatilemaking it possible to assemble highly efficient computing systems in confined spaces.
Of the two formats, Mini ITX is particularly popular among computer enthusiasts who aspire to create compact systems without compromising performance. This format is well received for its ability to incorporate all the necessary components in a small spacewhile maintaining a high level of efficiency and functionality.
Likewise, the format Mini ATX, despite being slightly larger than the Mini ITX, offers a good combination of compactness and functionality. Both of these motherboard variants allow users to explore a wide spectrum of options in terms of system configuration, while ensuring good airflow and adequate cooling, which are crucial for maintaining optimal system performance.
Additionally, as technology advances, these motherboards continue to evolve, featuring improved connectivity and support for the latest generation hardware components. The desire to reduce space footprint without sacrificing power and versatility is a growing trend in the world of PC buildingand Mini ATX and Mini ITX motherboards represent ideal solutions to meet this need.
Choosing the right motherboard: factors to consider
Choosing the right motherboard is a fundamental operation in the assembly process of a personal computer, as it represents the heart of the system on which all the other components will be installed. One of the first aspects to evaluate is the format of the motherboard, which can vary from ATX, Micro-ATX to Mini-ITX.
This choice will affect the size of your PC and the amount of expansion you can do in the future. Another determining factor is the type of processor you want to use; It is essential that the motherboard is compatible with the chosen processor, both in terms of socket and chipset. The expansion options available are a further element to carefully consider. In the next paragraphs we will delve deeper into this important aspect, which includes:
Some motherboards also offer advanced options such as support for RAID or overclocking. The available budget is another key factor in choosing the motherboard. There are motherboards to suit every budget, but it’s important to keep in mind that an investment in a quality motherboard can result in greater longevity and stability of your system. Finally, it may also be useful to consider other factors such as the presence of integrated networking functions, onboard audio and available cooling options, in order to build a system that best meets your needs.
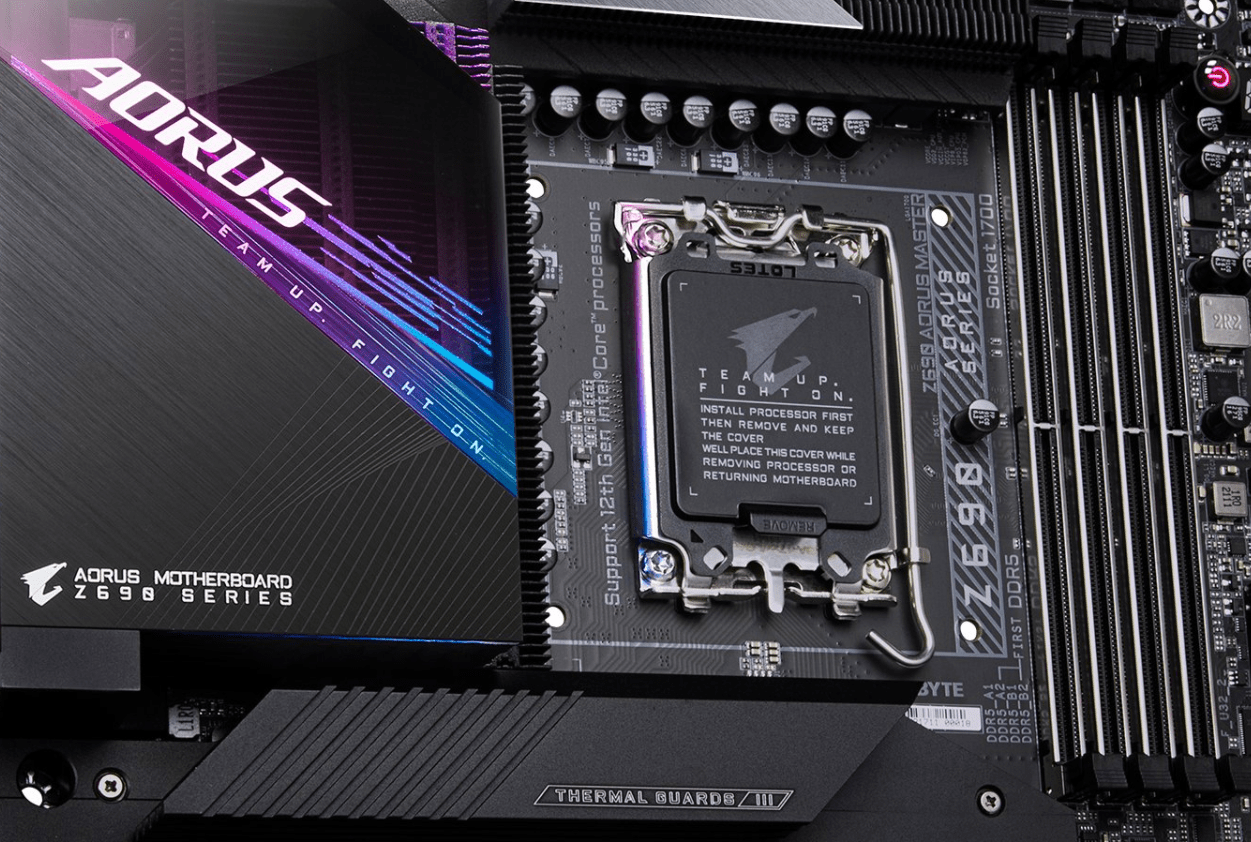
Processor compatibility
The compatibility of the processor with the motherboard is a crucial aspect to evaluate when you are configuring or upgrading a computer system. The primary connection point between these two critical components is the processor socket, which must match the one available on the motherboard.
Each processor is designed to fit into a certain type of socket, which in turn must be supported by the motherboard you choose. Furthermore, Processor generation is another key factor to consideras different generations of processors may have different power, cooling, and feature requirements that affect their compatibility with various motherboards.
For example, a motherboard that supports a socket LGA 1150 it will not be compatible with a processor that requires a socket LGA 1151. Additionally, some motherboards may be designed to only work with certain generations of processors, even if the socket looks the same. This may be due to differences in motherboard chipsets or other technical specifications that may affect communication between the processor and the motherboard.
Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the motherboard you choose supports not only the desired processor socket, but also its generation, to ensure smooth communication and effective system operation. A thorough check of the technical specifications and, if necessary, a consultation with industry experts or the manufacturer’s customer service department can help avoid costly and frustrating incompatibilities, while ensuring that the system is able to operate to its maximum potential.
Expansion options
The expansion options…















Leave a Reply
View Comments