AMD has shared in detail all the technical specifications and improvements of the new series of Ryzen 5000 desktop CPUs, with Zen 3 architecture
After seeing the main changes in the Ryzen 5000 series announced at today’s conference, AMD shared in detail all technical specifications and improvements over Zen 2.
AMD Ryzen 5000: supported RAM memories, TDP and integrated heatsink
All four processors support RAM with speeds up to DDR4-3200, and TDPs of 105 W will allow to reach turbo power of 142 W, equal to the current Ryzen processors. AMD has decided to include heatsinks only with 65 W or less processors, stating that users buying higher-end models still prefer to use custom heatsinks to maximize performance.
If they had included 125W heatsinks with 105W processors, they would have had to lower the frequencies to compensate. For the 5000 series, the IO die remains the same as in previous generations. There remains therefore support a PCIe 4.0, and NVMe / SATA allocation.

Availability to launch and measures against bots and scalpers
AMD said that after the public response when the 16-core model was announced later in the last generation, the company aimed this time for a unified launch. When asked about the quantities available at launch, especially considering all the orders to TSMC related to the consoles, the company however he preferred not to answer.
However, he said he is working hard with distributors to manage bots and scalpers. The goal is obviously to avoid the disaster the launch of NVIDA’s next-gen consoles and new Ampere GPUs, sold out instantly and then resold at insane prices.
AMD Ryzen 5000: This is why the 4000 series was skipped
As for the name, it’s easy to see that the latest desktop processor series was the 3000, ed the 4000 series was therefore skipped. AMD’s Robert Hallock said the company has already launched APUs under the name Ryzen 4000, still based on Zen 2. AMD therefore wanted to make sure the new series was easily recognizable with a different nomenclature. As a further motivation, the number 4 in China is considered unfortunate, having a similar pronunciation to the word ‘death’.
AMD’s promise: Significant performance increases every year
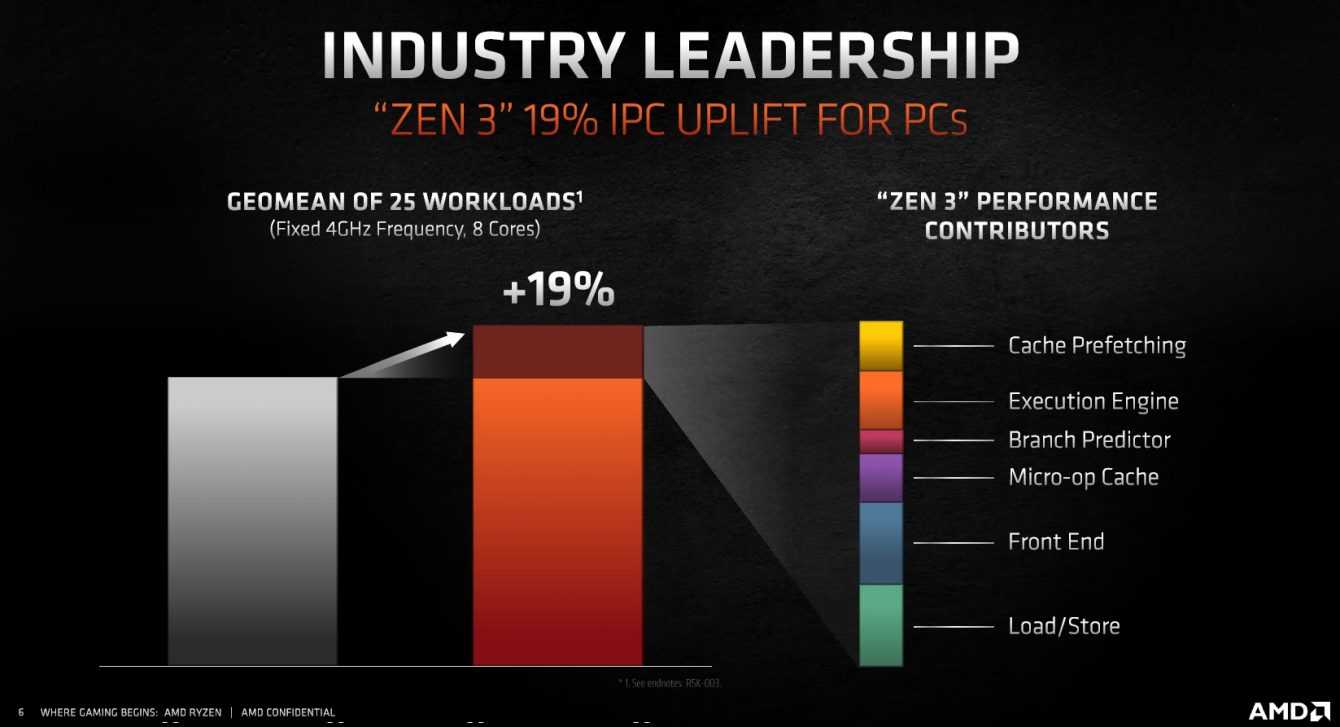
AMD wanted to emphasize its claim to be the only desktop CPU company to guarantee products every year which actually greatly improve performance. The keyword of the announcement was indeed +19% performance compared to the previous generation. The increase is in both single-thread and multi-thread performance.
The company claims it has a product that can beat Intel in all work scenarios that interest users. That 19% comes from 25 both real and synthetic benchmarks. Comparisons were made between the Ryzen 9 3900X, the previous generation 12-core processor and the Ryzen 9 5900X, the latest generation 12-core processor, both at fixed frequencies of 4.0 GHz and with DDR4-3600 RAM.
In particular, the increase should be guaranteed by a sum of various smaller improvements:
- +2.7% Cache Prefetching
- +3.3% Execution Engine
- +1.3% Branch Predictor
- + 2.7% Micro-op Cache
- +4.6% Front End
- +4.6% Load/Store
For now, he has not specified how these improvements have been achieved, but has confirmed that he will reveal it in time for the release of the CPUs. But what he wanted to point out is that the new Zen 3 architecture is a redesign a 360 degrees of Zen 2.
As expected from Zen 3, AMD has combined two 4-core structures (CCX) in a single 8-core structure. This means that each of the eight cores will have access to 32MB of L3 cache, with significantly improved latency for each core as it moves from 16MB to 32MB. Previously, going over 16MB with one core, it ended up in main memory, much slower.
AMD Ryzen 5000: 7nm manufacturing process
Speaking of the manufacturing process, AMD clarified that the processors will use the same a 7 nm at TSMC Ryzen 3000XT series. Finally, AMD claims to be able to guarantee an increase of 2.4 times in performance per watt compared to the first Ryzen series, or an increase of 2.8 times compared to Intel Comet Lake.

For other news, guides, reviews and specials on the hardware world, go to the dedicated section on our site! Remember to also follow us on our Instagram, Facebook and Twitter, and on our Youtube and Twitch channels!















